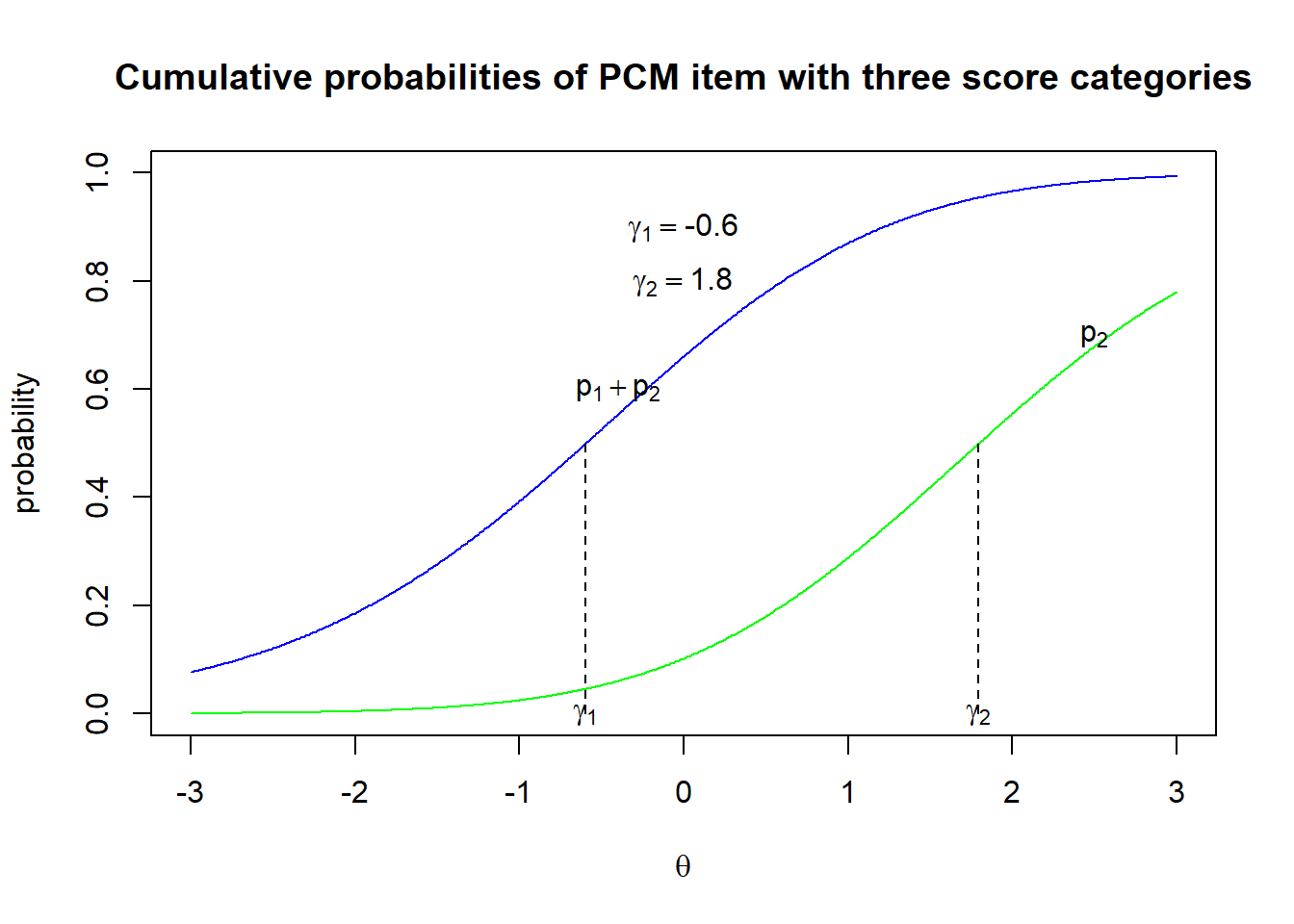
Given the difficulty of interpreting the Andrich thresholds in terms of difficulty, Thurstonian thresholds allow us to to perceive category success in terms of item step difficulties. Thurstonian thresholds are defined as the ability at which students have 50% chance of obtaining a score or higher scores. For example, for an item with 0, 1 and 2 scores, the first Thurstonian threshold is the ability at which the students have 50% chance of getting a 1 or 2.
In Figure 25.1, γ1 (= -0.6) is the ability at which students have 50% chance of obtaining a score of 1 or 2 (or, at least 1), while γ2 (= 1.8) is the ability at which students have 50% chance of obtaining a score of 2 (or, at least 2, but 2 is the maximum score in this example). Comparing the deltas with the gammas, where δ1 = -0.5, δ2 = 1.7, and γ1 = -0.6, γ2 = 1.8, the differences between deltas and gammas are not very large.
Extension activity
Reproduce Figure 25.1 from the Partial Credit Model equations. Try differing values of the thresholds and see how the curves change.
Andrich, David, and Ida Marais. 2019.
“The Idea of Measurement.” In
A Course in Rasch Measurement Theory, 3–11. Springer Nature Singapore.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7496-8_1.
Bond, Trevor G., Zi Yan, and Moritz Heene. 2020.
Applying the Rasch Model: Fundamental Measurement in the Human Sciences. Routledge.
https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429030499.
Cappelleri, Jason Lundy, J. C. 2014.
“Overview of Classical Test Theory and Item Response Theory for the Quantitative Assessment of Items in Developing Patient-Reported Outcomes Measures.” Clinical Therapeutics 36 (5): 648–62. https://doi.org/
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.04.006.
Cronbach, Lee J. 1951.
“Coefficient Alpha and the Internal Structure of Tests.” Psychometrika 16 (3): 297–334.
https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02310555.
Goldstein, H., and Steve Blinkhorn. 1982.
“The Rasch Model Still Does Not Fit.” British Educational Research Journal 8 (2): 167–70.
https://doi.org/10.1080/0141192820080207.
Lord, Frederic M, and Melvin R Novick. 2008. Statistical Theories of Mental Test Scores. IAP.
McNeish, Daniel. 2018.
“Thanks Coefficient Alpha, We’ll Take It from Here.” Psychological Methods 23 (3): 412–33.
https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000144.
Panayides, Panayiotis, Colin Robinson, and Peter Tymms. 2010.
“The Assessment Revolution That Has Passed England by: Rasch Measurement.” British Educational Research Journal 36 (4): 611–26.
https://doi.org/10.1080/01411920903018182.
Robitzsch, Alexander, Thomas Kiefer, and Margaret Wu. 2022.
TAM: Test Analysis Modules.
https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=TAM.
Sijtsma, Klaas. 2008.
“On the Use, the Misuse, and the Very Limited Usefulness of Cronbach’s Alpha.” Psychometrika 74 (1): 107–20.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11336-008-9101-0.
Wright, Benjamin D, and Magdalena Mok. 2000. “Rasch Models Overview.” Journal of Applied Measurement 1 (1): 83–106.